

That’s why price competition is fierce, and retailers have to focus on cutting down costs to attract customers into their stores. In the UK alone, customers can choose from over 87,000 physical grocery stores. Exit barriers: If it is difficult or costly to leave an industry, firms will remain and add to the intensity of competition by trying to secure their market share.Įxamples of highly competitive industries.Profit margins tend to be low, and production takes place at marginal cost. The number of competitors: The higher the number of competitors, the greater the intensity of competition.The intensity of an industry’s competition can be evaluated with the following parameters: Performance competition focuses on product quality and additional service offerings instead of price.Price competition refers to market players trying to undercut each other with lower prices by increasing the efficiency in their value chain.High competition intensity can result from two main factors: Price competition and performance competition. Central questions about the number of competitors and the nature of potential threats need to be answered.
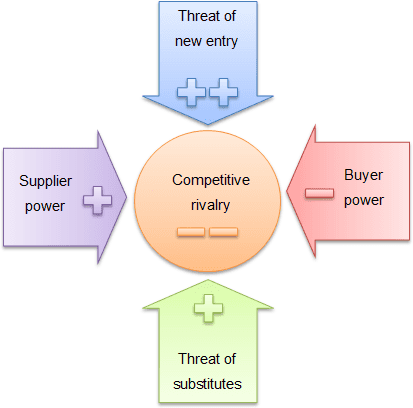
The main purpose of the 5 Forces Analysis is to assess the competitive situation in an industry. As such, the 5 Forces is also an ideal framework for evaluating potential investment strategies. The results can be used to derive whether and to what extent the industry under consideration is attractive for a company.

Only then can data be effectively collected and reliably used for a company’s decision-making.įinally, the 5 Forces Analysis leads to an assessment of the threats posed by potential competitors and substitutes, as well as the bargaining power of suppliers and customers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
